How Do You Make SAP Technically Fit for Modern Mobility Web Services? In Just a Few Steps Using SAP Transactions SE80 and SOA Manager.
Accessing SAP Externally
If you want to give external systems access to SAP function modules, various ways offer themselves. A rather conventional path is via the RFC interface. SAP offers native libraries for this on various platforms, which can then in turn be called up by language-dependent libraries, e.g., for Java. Unfortunately, these libraries are not available for all platforms and programming languages. For example, access via mobile devices or browsers must take place via a server-side intermediate component.
Publishing SAP Web Services
Publishing SAP function modules as a web service provides a remedy. Since these are based on HTTP, they can be called up by almost any network-capable application. A further advantage is the more convenient integration of web services into existing heterogeneous service-oriented system landscapes, in which communication currently takes place largely via web services.
How It Works
The following example illustrates how simply and conveniently SAP enables the provision of function modules as a SOAP web service with its tools. The usual path is described here, without going into the actually quite diverse configuration options in the individual steps.
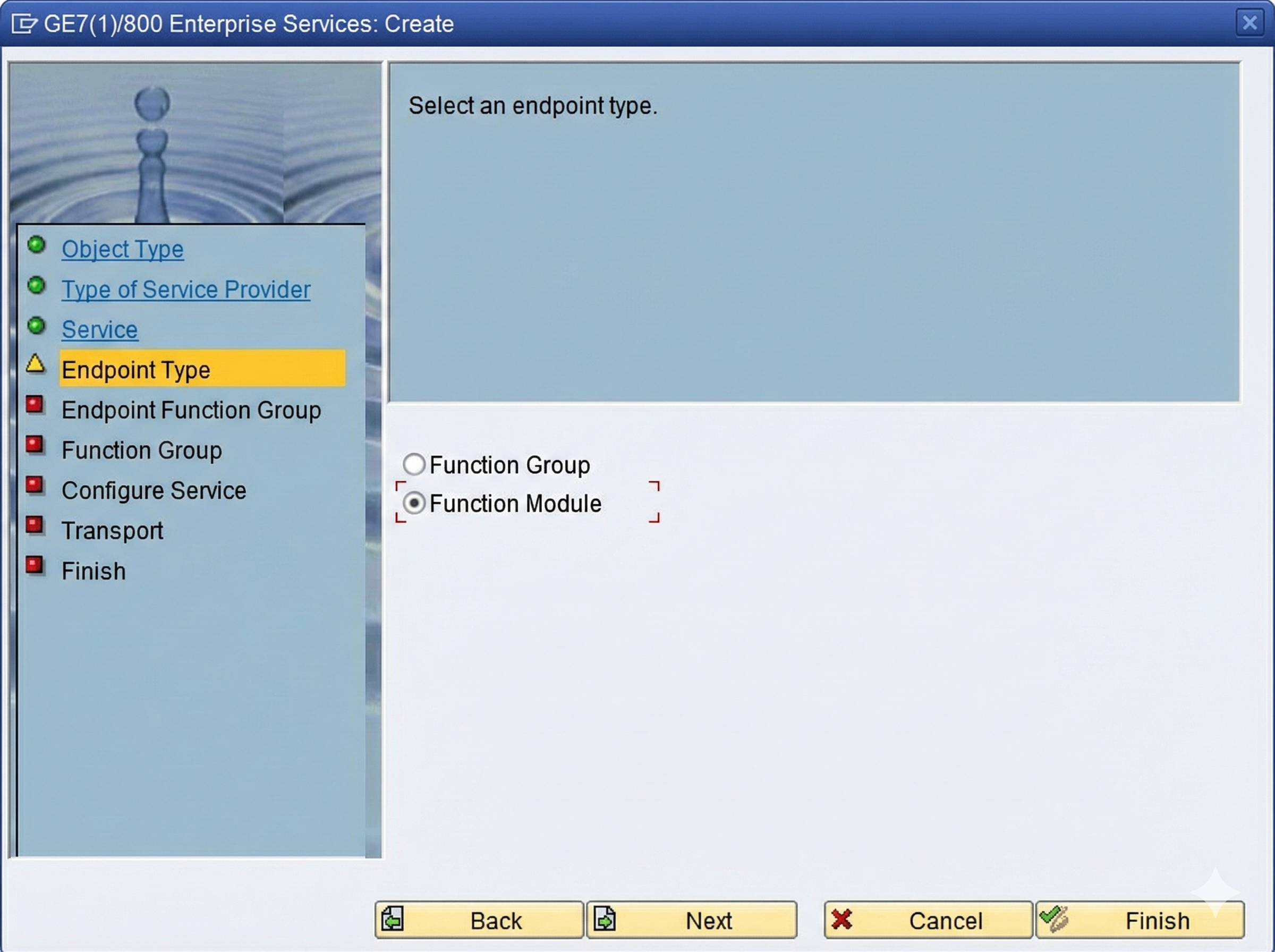
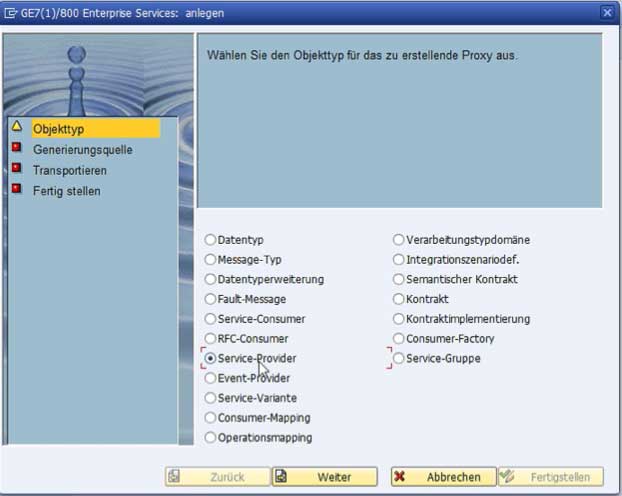
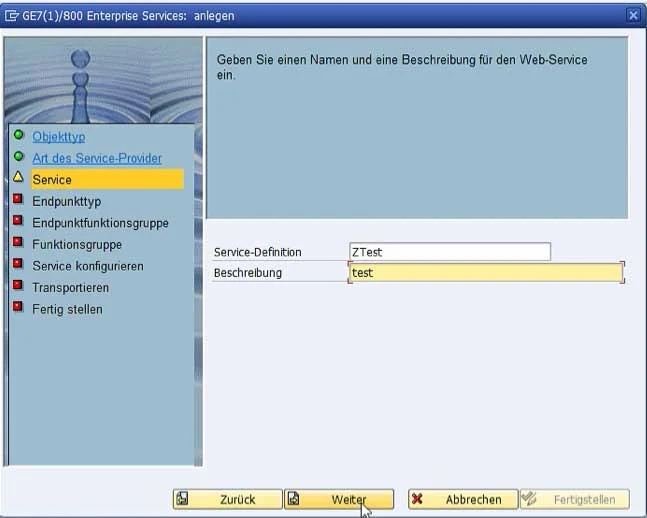
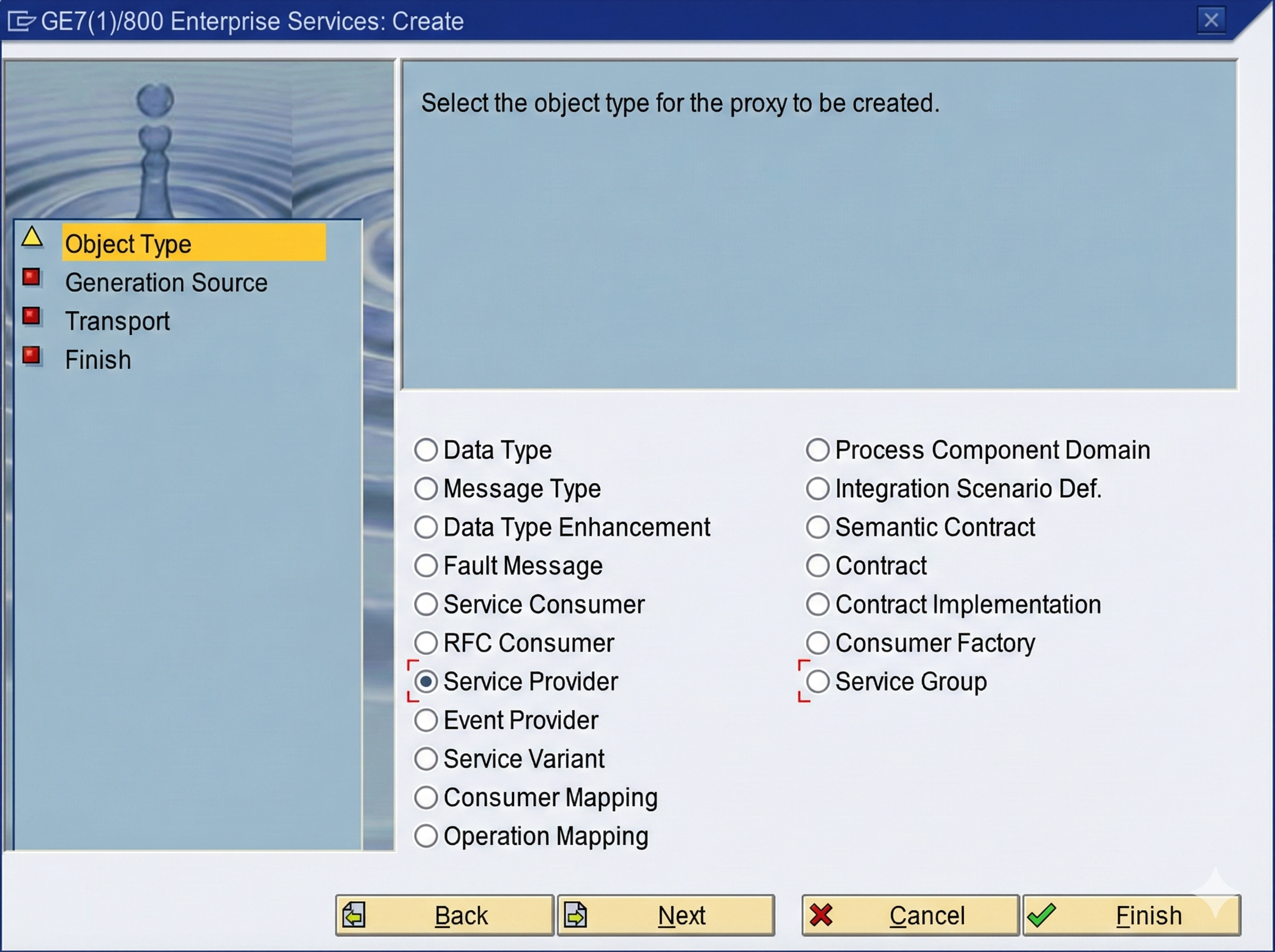
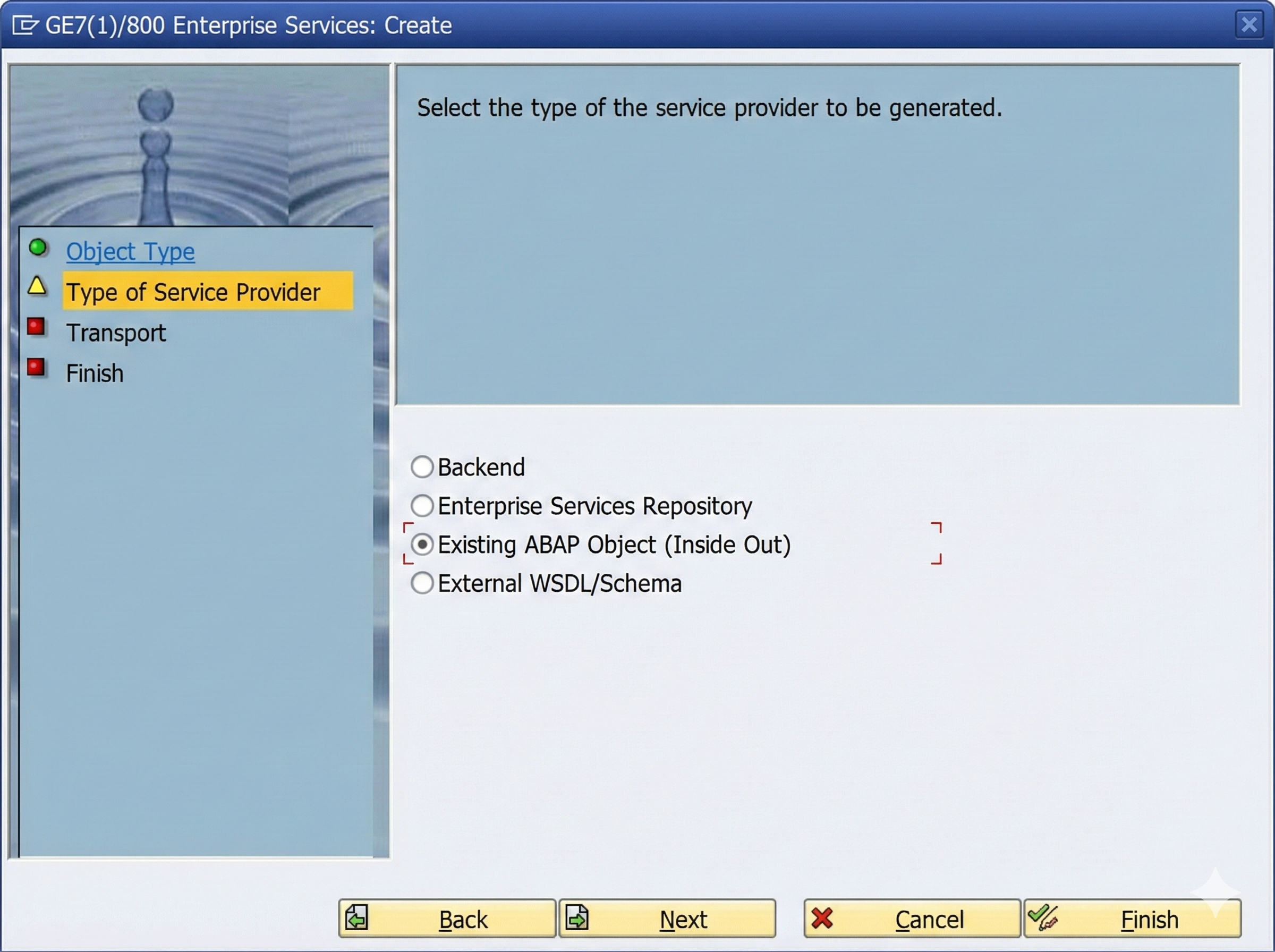
The definition of the web service takes place in the Object Explorer. This can be opened via transaction SE80. After selecting a target package in the Repository Browser, the wizard for creating the web service can be started via the context menu "Create > Enterprise Service".
Fig. 1: Select Service Provider as object type
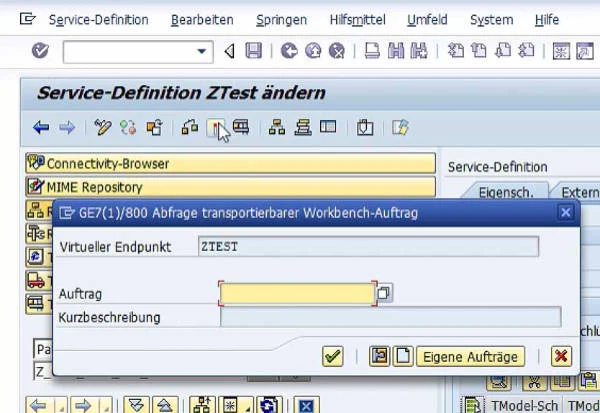
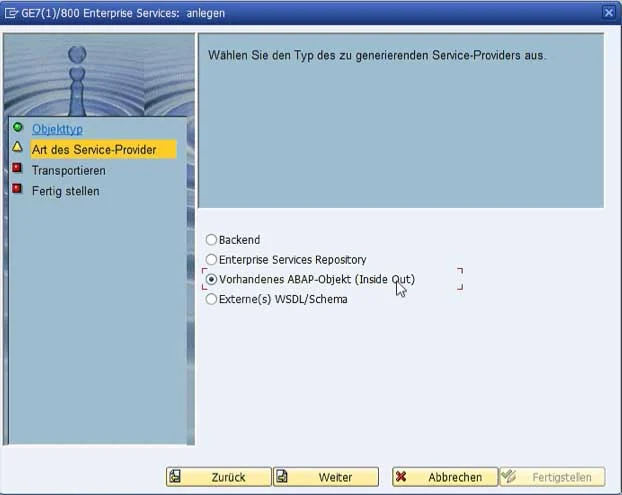
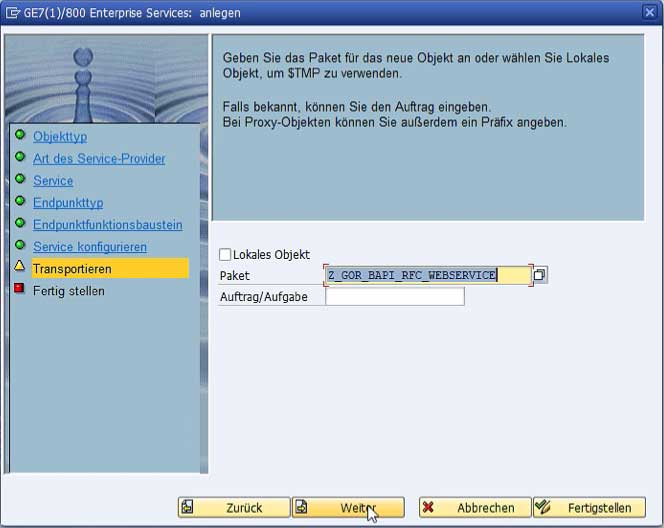
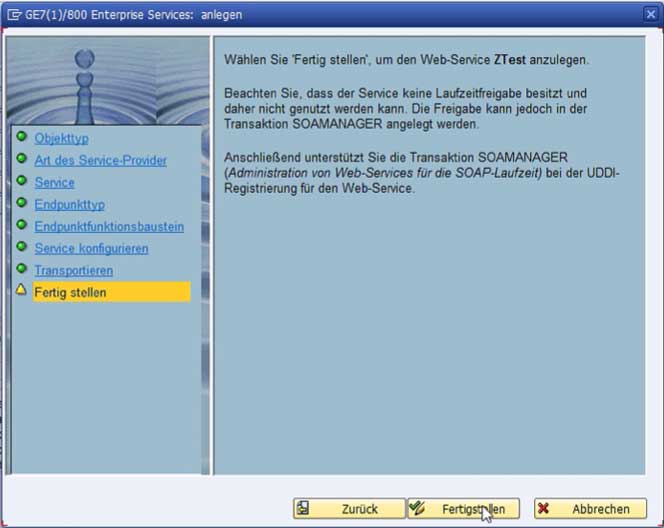
The service is now located in the selected package and can be activated in the menu bar via an existing or new workbench request.
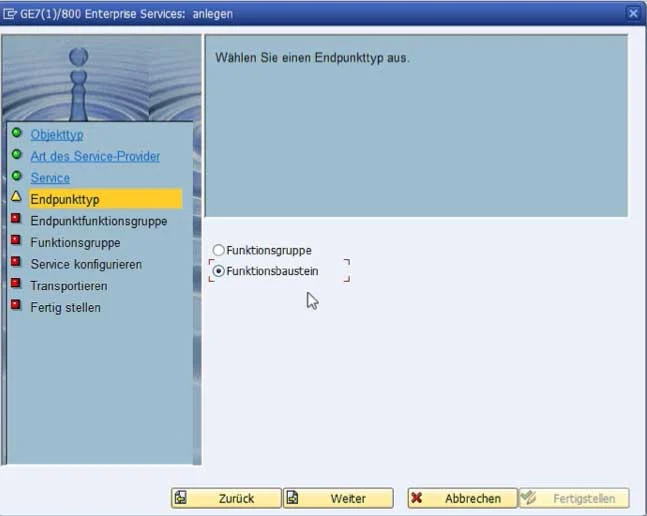
After activation, the web service still requires a runtime release for final use. This is configured in the SOA Manager. This is accessible via the SAP transaction "SOA-Manager".
.png)
After selecting "Web Service Configuration," the service to be configured can be selected via a search for the object type "Service Definition" and the corresponding object name.
.png)
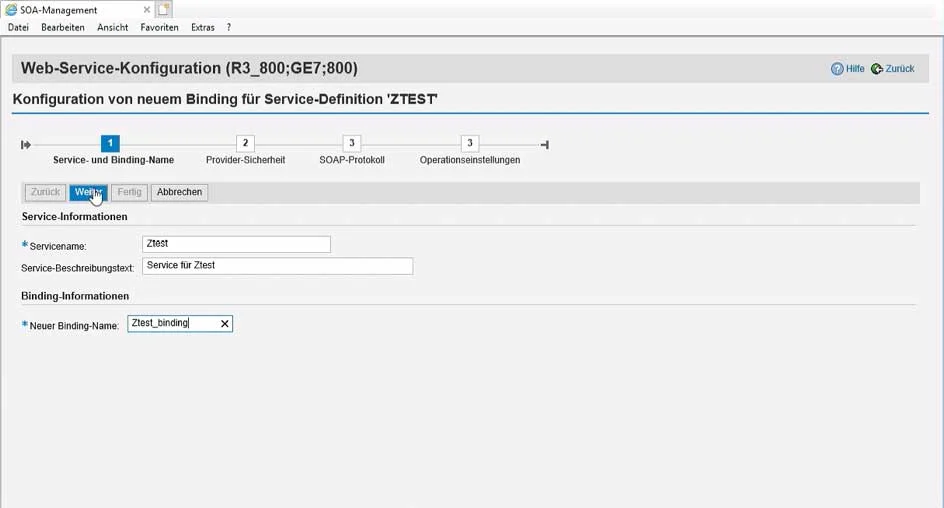
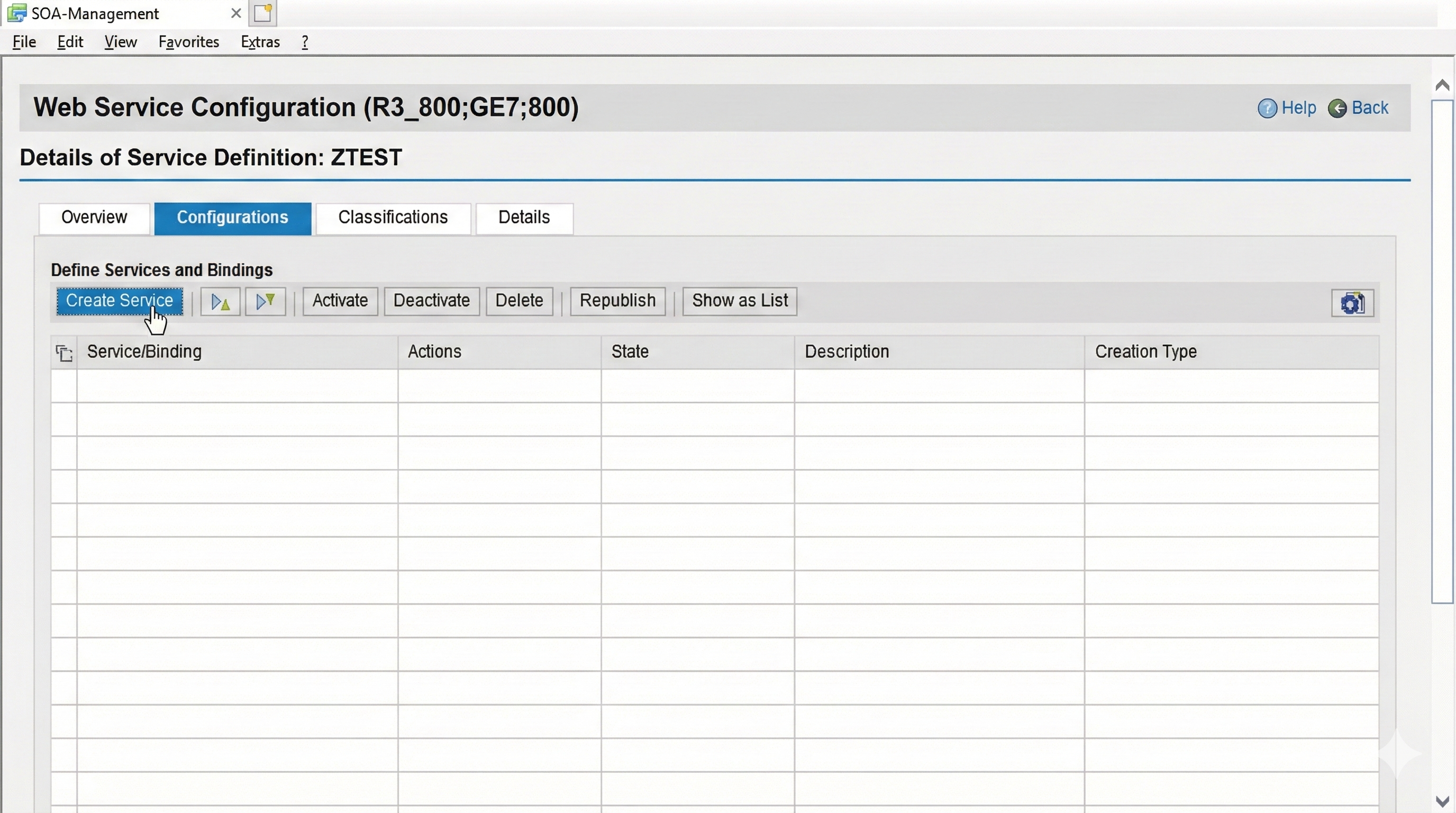
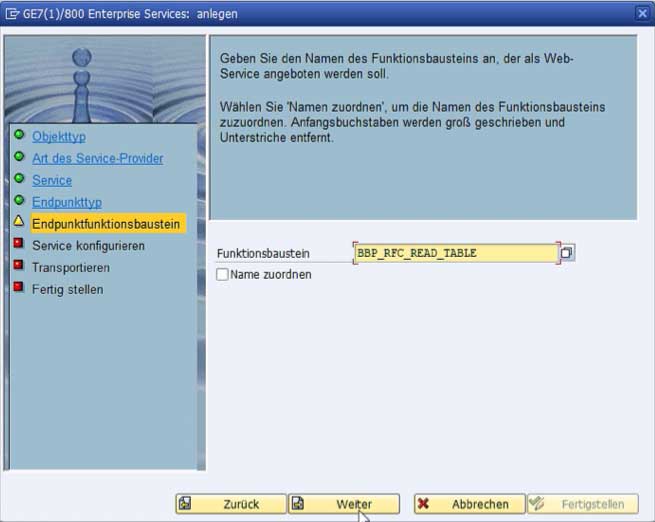
Selecting the service opens the wizard for configuring the web service release via the "Create Service" button.
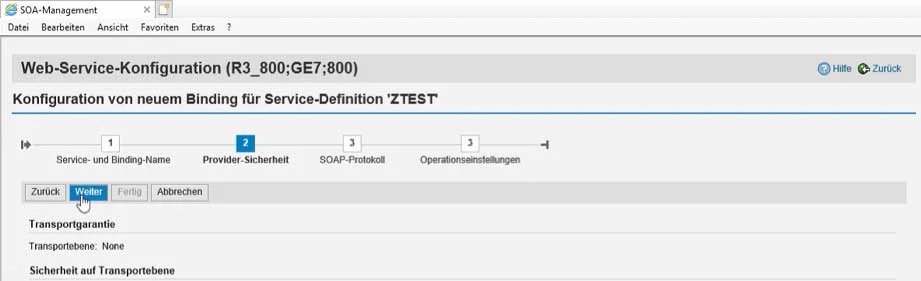
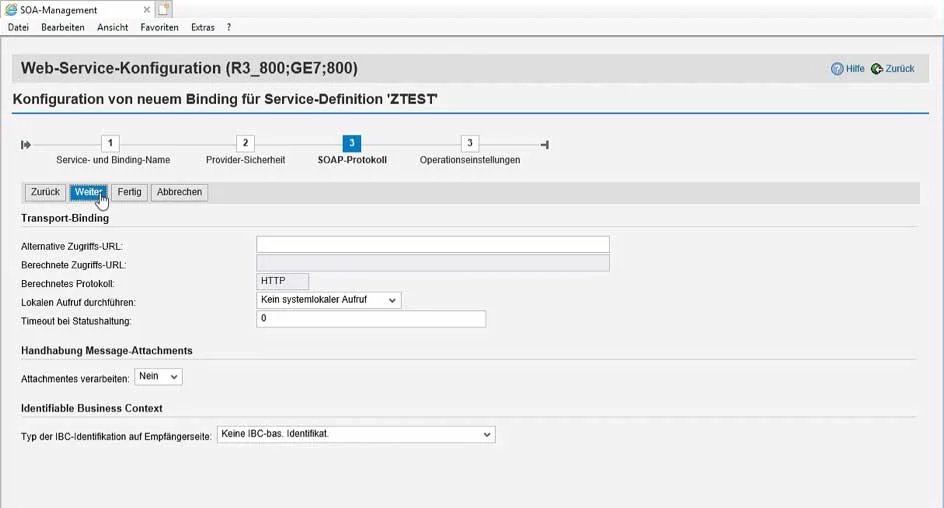
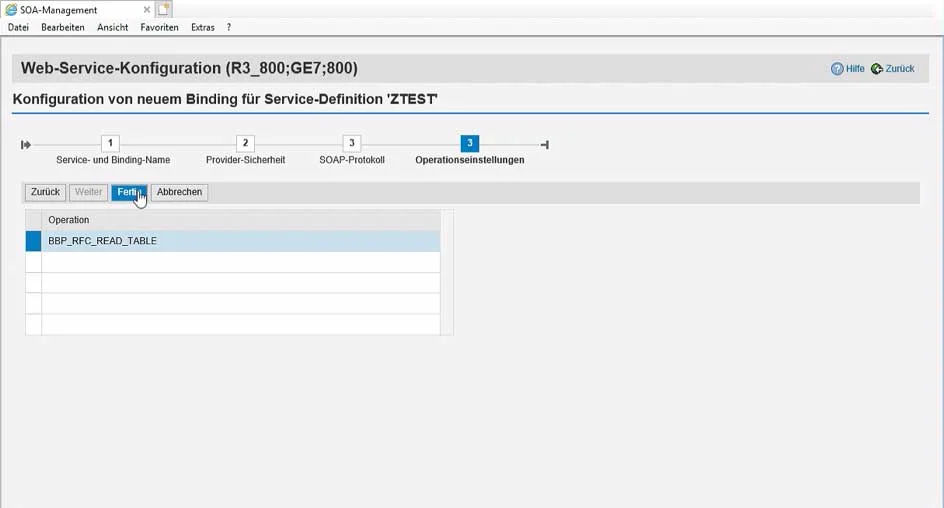
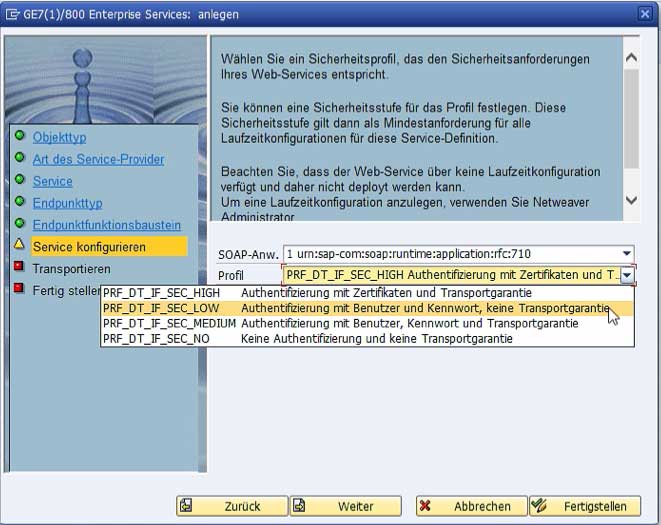
In the wizard for configuring the release, which consists of four steps, SOAP-relevant settings, e.g., regarding security, are made:
Fig. 1: Entry of the service name and name of the binding (usually with the suffix "_binding")
The result of the wizard can be seen in the configuration list. There, the service can later be deactivated, edited, and deleted.
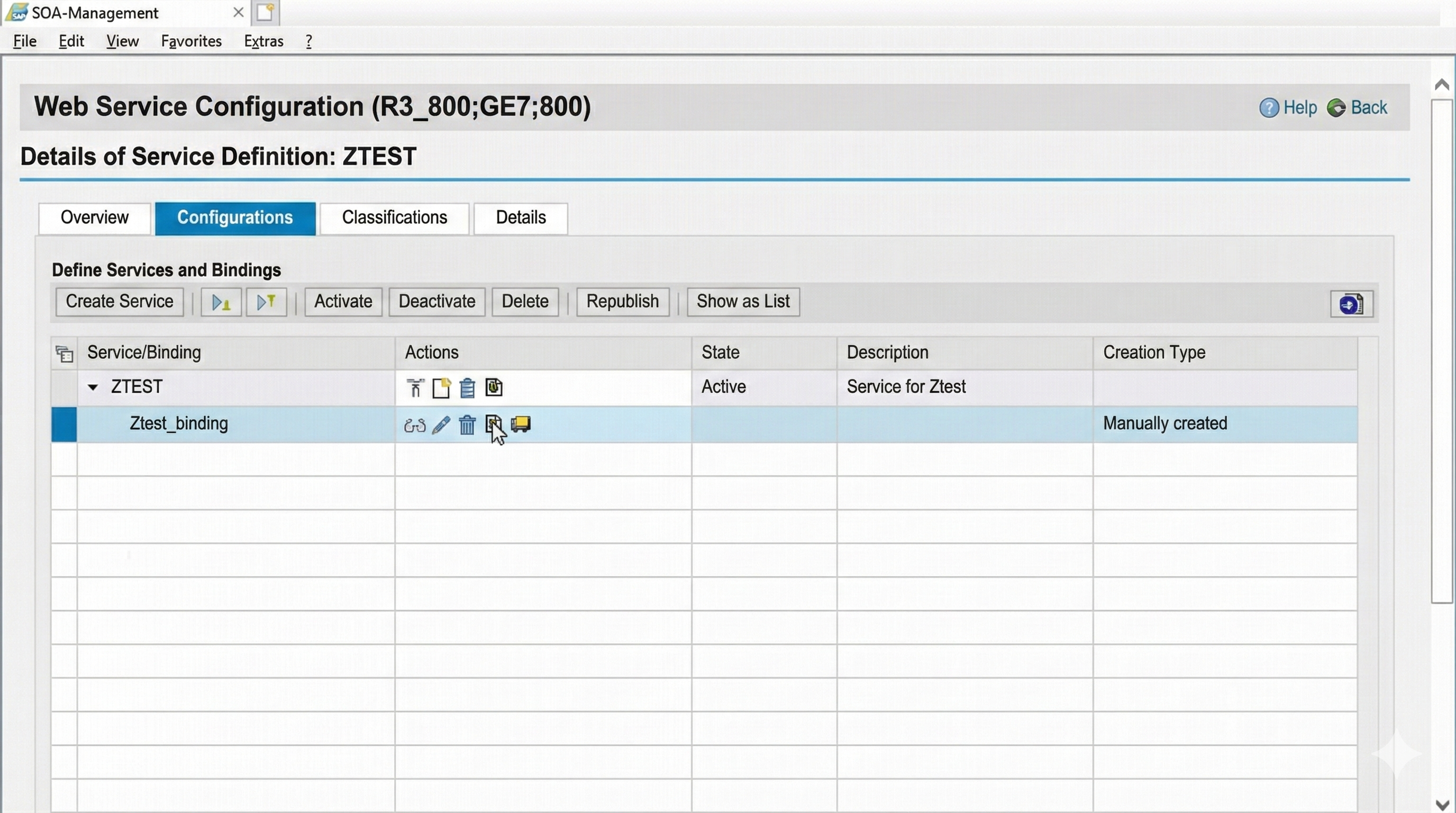
So that applications can access the web service, they now only need the URL of the WSDL of the web service. This information can be displayed via the corresponding symbol in the binding entry in the list.
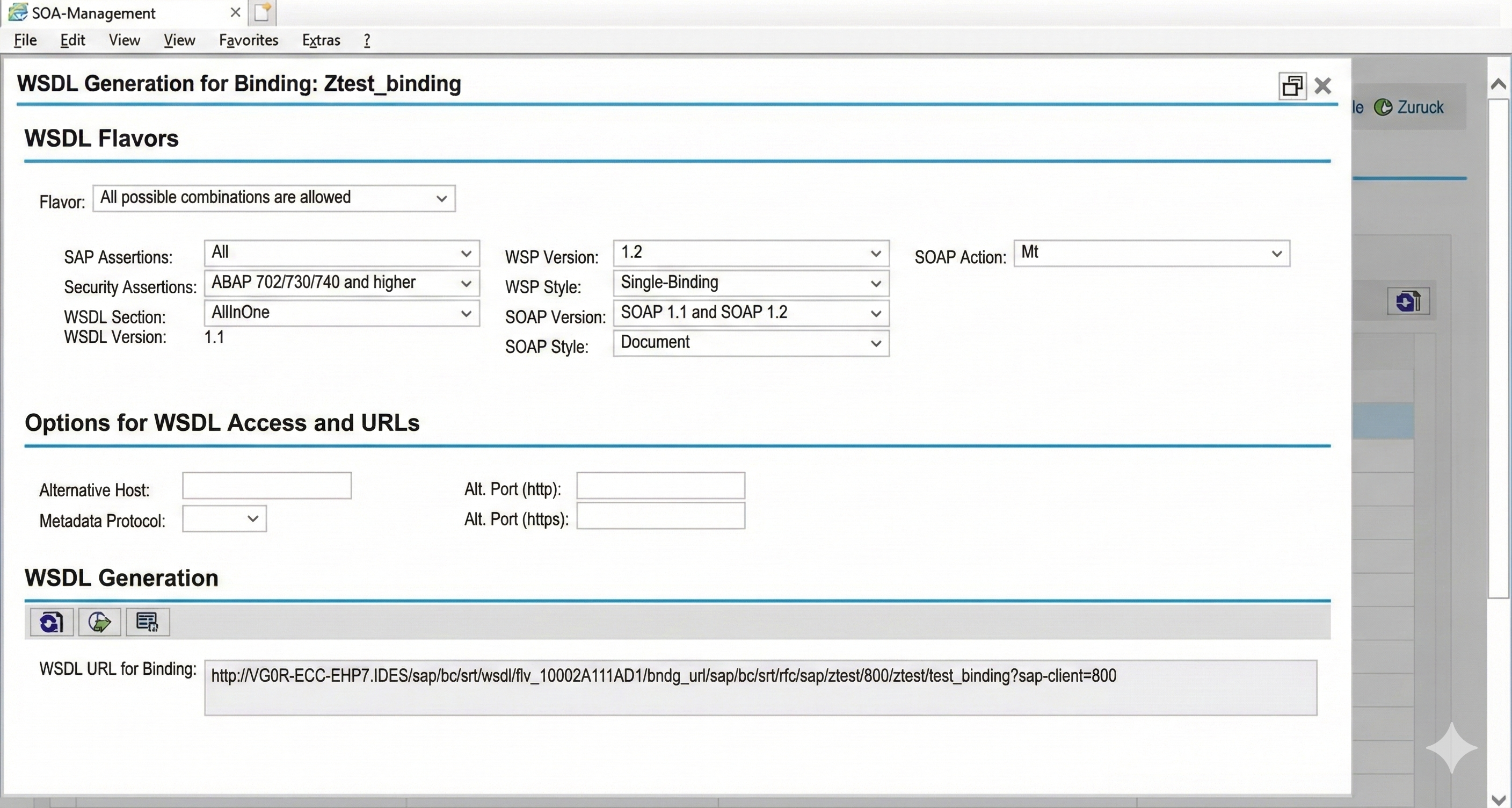
Conclusion
Configuring SAP for web services requires only a few steps. With transactions SE80 and SOA Manager, a convenient solution for SAP Mobility connection is thus available, without having to take the path via the RFC interface or a middleware component.

Live in 90 days
Optimize your warehouse effortlessly and cost-effectively with the Ontego subscription model.

 and a description.png)